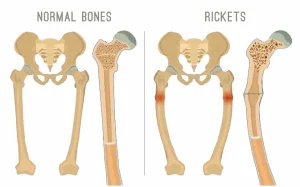
Overview
Rickets is a childhood bone disorder characterized by softening and weakening of the bones due to inadequate mineralization. It most commonly results from a deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate, which are essential for healthy bone development. Rickets primarily affects infants and young children during periods of rapid growth and can lead to bone deformities if not treated early.
Symptoms of Rickets
Symptoms often develop gradually and become more noticeable as the condition progresses.
-
Delayed growth and short stature
-
Bone pain or tenderness
-
Soft skull bones in infants
-
Delayed closure of the fontanelles
-
Bowed legs or knock knees
-
Thickening of wrists, ankles, or ribs
-
Delayed tooth eruption or dental problems
-
Muscle weakness
Causes of Rickets
Rickets occurs when bones do not receive enough minerals to harden properly.
Common causes include:
-
Vitamin D deficiency due to limited sunlight exposure
-
Inadequate dietary intake of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate
-
Malabsorption disorders affecting nutrient absorption
-
Chronic kidney or liver disease
-
Rare genetic conditions affecting vitamin D metabolism
Risk Factors for Rickets
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing rickets in children.
-
Prolonged exclusive breastfeeding without vitamin D supplementation
-
Limited sun exposure
-
Darker skin pigmentation
-
Premature birth
-
Poor nutrition or restrictive diets
-
Chronic gastrointestinal or kidney conditions
Complications of Rickets
If left untreated, rickets can lead to long-term skeletal and health problems.
-
Permanent bone deformities
-
Short stature in adulthood
-
Increased risk of bone fractures
-
Dental abnormalities
-
Delayed motor development
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent most complications.
Prevention of Rickets
Rickets is largely preventable through proper nutrition and sunlight exposure.
-
Adequate intake of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate
-
Vitamin D supplementation for infants and high-risk children
-
Safe and regular exposure to sunlight
-
Balanced diet including fortified foods
-
Regular pediatric check-ups to monitor growth and bone health
Preventive measures play a key role in ensuring healthy bone development and reducing the risk of rickets.
Advertisement