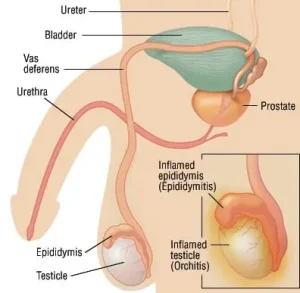
Overview
Orchitis is an inflammatory condition of one or both testicles, most commonly caused by infection. It can occur suddenly and may be painful, leading to swelling and discomfort in the scrotum. Orchitis often develops as a complication of viral or bacterial infections and may occur alone or together with inflammation of the epididymis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of orchitis can range from mild to severe and may develop rapidly:
-
Testicular pain or tenderness
-
Swelling of one or both testicles
-
Scrotal redness or warmth
-
Fever and chills
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Pain during urination
-
Discomfort during sexual activity
-
General feeling of illness
Causes
Orchitis is most commonly caused by infections:
-
Viral infections, particularly mumps
-
Bacterial infections spreading from the urinary tract
-
Sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia or gonorrhea
-
Prostate or epididymal infections extending to the testicles
-
Rarely, trauma or autoimmune reactions
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing orchitis:
-
Not being vaccinated against mumps
-
History of urinary tract infections
-
Sexually transmitted infections
-
Unprotected sexual activity
-
Recent urinary catheter use
-
Structural abnormalities of the urinary tract
Complications
Orchitis can lead to complications, especially if not treated promptly:
-
Testicular atrophy
-
Chronic testicular pain
-
Abscess formation
-
Reduced fertility or infertility
-
Spread of infection to surrounding tissues
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on reducing infection risk:
-
Receiving recommended vaccinations, including mumps
-
Practicing safe sex
-
Treating urinary or prostate infections promptly
-
Maintaining good personal hygiene
-
Seeking early medical care for scrotal pain or swelling
Advertisement