Overview
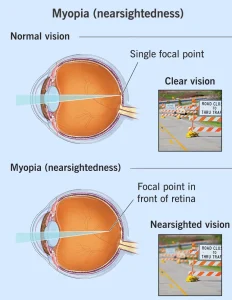
Nearsightedness, also known as myopia, is a common vision condition in which close objects are seen clearly, while distant objects appear blurred. It occurs when light entering the eye focuses in front of the retina instead of directly on it. Nearsightedness often begins in childhood or adolescence and may worsen as the eyes continue to grow. The condition can usually be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
Symptoms
Symptoms of nearsightedness may develop gradually and vary in severity:
-
Blurred vision when looking at distant objects
-
Squinting to see clearly
-
Eye strain, especially when driving or watching distant screens
-
Headaches caused by visual fatigue
-
Difficulty seeing road signs or classroom boards
Children may show signs such as sitting close to screens or holding books very close to the face.
Causes
Nearsightedness is caused by structural changes in the eye. The eyeball may be too long, or the cornea may be too curved, causing light to focus incorrectly. Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development. Extended periods of close-up activities, such as reading or screen use, are thought to influence progression, especially during childhood.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing nearsightedness:
-
Family history of myopia
-
Prolonged near work, including reading or digital device use
-
Limited time spent outdoors during childhood
-
Early onset during school-age years
The risk increases when genetic predisposition and environmental factors occur together.
Complications
If not properly corrected or monitored, nearsightedness may lead to complications:
-
Increased risk of retinal detachment
-
Glaucoma
-
Cataracts
-
Myopic macular degeneration in severe cases
-
Reduced quality of life due to visual limitations
Higher degrees of nearsightedness are associated with greater risk of eye-related complications.
Prevention
Nearsightedness cannot always be prevented, but certain measures may help reduce progression, especially in children:
-
Encouraging regular breaks during close-up activities
-
Increasing time spent outdoors
-
Ensuring proper lighting during reading or screen use
-
Scheduling regular eye examinations for early detection
-
Using prescribed corrective lenses as recommended
Early diagnosis and appropriate vision care play an important role in managing nearsightedness and protecting long-term eye health.
Advertisement