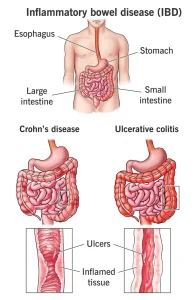
Overview
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic conditions characterized by ongoing inflammation of the digestive tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions cause periods of flare-ups and remission and can significantly affect digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall quality of life. IBD is not the same as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which does not involve inflammation or permanent damage to the intestines.
Symptoms
-
Chronic diarrhea, sometimes with blood or mucus
-
Abdominal pain and cramping
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Unintended weight loss
-
Reduced appetite
-
Rectal bleeding
-
Urgency to have bowel movements
-
Fever during active inflammation
Causes
The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but it is believed to result from an abnormal immune response. Contributing factors include:
-
Immune system dysfunction that attacks the digestive tract
-
Genetic susceptibility
-
Environmental triggers such as infections or diet
-
Altered gut microbiome
Risk factors
-
Family history of inflammatory bowel disease
-
Age, commonly diagnosed before 30 years
-
Smoking, especially increases risk and severity of Crohn’s disease
-
Use of certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
-
Urban living and Western-style diets
Complications
-
Intestinal strictures or blockages
-
Fistulas, particularly in Crohn’s disease
-
Increased risk of colon cancer, especially with long-standing disease
-
Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
-
Osteoporosis
-
Extraintestinal complications affecting the skin, eyes, or joints
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent IBD, but strategies that may help reduce flare-ups and complications include:
-
Adhering to prescribed medical treatment plans
-
Avoiding smoking
-
Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
-
Managing stress through relaxation techniques or counseling
-
Regular medical follow-up and screening for complications
With appropriate medical care and lifestyle management, many individuals with IBD can achieve long periods of remission and maintain a good quality of life.
Advertisement