Overview
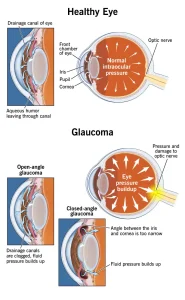
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, which is essential for clear vision. This damage is often associated with increased pressure inside the eye, although glaucoma can also occur with normal eye pressure. Glaucoma usually develops slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent vision loss or blindness.
Symptoms
Symptoms of glaucoma depend on the type and stage of the condition. In many cases, early stages cause no obvious symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
-
Gradual loss of peripheral vision
-
Tunnel vision in advanced stages
-
Eye pain or pressure, especially in acute forms
-
Blurred vision
-
Halos around lights
-
Redness of the eye
-
Nausea or vomiting in severe cases
Sudden symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Causes
Glaucoma occurs when increased pressure inside the eye damages the optic nerve. This pressure builds up when fluid in the eye does not drain properly. Causes may include:
-
Blockage or reduced drainage of eye fluid
-
Overproduction of eye fluid
-
Poor blood flow to the optic nerve
-
Genetic factors
-
Eye injury or inflammation
Different mechanisms are involved depending on the specific type of glaucoma.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing glaucoma, including:
-
Age over 40
-
Family history of glaucoma
-
High intraocular pressure
-
Diabetes
-
High blood pressure
-
Long-term use of corticosteroid medications
-
Previous eye injuries
-
Certain ethnic backgrounds
Regular eye exams are especially important for individuals with risk factors.
Complications
If glaucoma is not diagnosed and treated early, it can lead to serious complications, such as:
-
Permanent vision loss
-
Complete blindness
-
Reduced ability to perform daily activities
-
Decreased quality of life
Vision loss caused by glaucoma cannot be reversed, making early detection critical.
Prevention
While glaucoma cannot always be prevented, steps can help reduce the risk of vision loss:
-
Undergoing regular comprehensive eye examinations
-
Following prescribed treatment plans if diagnosed
-
Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure
-
Protecting eyes from injury
-
Informing eye care providers about family history
Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are the most effective ways to prevent vision loss related to glaucoma.
Advertisement