Overview
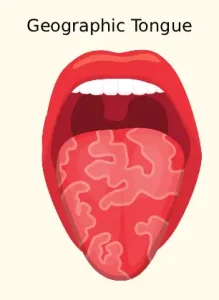
Geographic tongue is a harmless inflammatory condition that affects the surface of the tongue. It is characterized by irregular, smooth, red patches surrounded by white or light-colored borders, giving the tongue a map-like appearance. These patches may change shape, size, and location over time. Geographic tongue is not contagious and is generally considered a benign condition, although it may cause discomfort in some individuals.
Symptoms
Symptoms of geographic tongue vary from person to person and may come and go. Common symptoms include:
-
Smooth, red patches on the tongue
-
White or pale borders surrounding the red areas
-
Map-like patterns that change location over time
-
Burning or stinging sensation, especially with spicy, acidic, or hot foods
-
Increased tongue sensitivity
-
Mild discomfort or pain in some cases
Many people with geographic tongue have no symptoms other than visible changes.
Causes
The exact cause of geographic tongue is not clearly understood. It is believed to result from inflammation and loss of tiny finger-like projections on the tongue surface. Possible contributing factors include:
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Allergic conditions
-
Emotional stress
-
Hormonal changes
-
Vitamin deficiencies, especially B vitamins
-
Association with certain skin conditions
In many cases, no specific cause can be identified.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the likelihood of developing geographic tongue, including:
-
Family history of the condition
-
Presence of fissured tongue
-
Allergies or asthma
-
Psoriasis or other inflammatory skin disorders
-
Stress or anxiety
Geographic tongue can affect individuals of all ages.
Complications
Geographic tongue is not a serious condition and usually does not lead to medical complications. However, possible issues include:
-
Persistent oral discomfort or burning
-
Sensitivity to certain foods
-
Anxiety or concern due to the appearance of the tongue
The condition does not increase the risk of oral cancer or infection.
Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent geographic tongue, but certain measures may help reduce discomfort and flare-ups:
-
Avoiding foods that trigger irritation
-
Maintaining good oral hygiene
-
Managing stress effectively
-
Addressing vitamin deficiencies if present
-
Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use
Regular dental checkups can help reassure individuals and rule out other tongue or oral conditions.
Advertisement