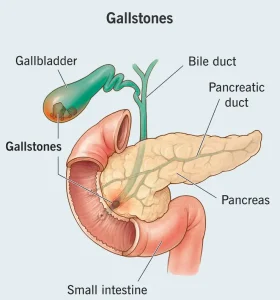
Overview
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. These stones can vary in size and number and may be made of cholesterol, bilirubin, or a mixture of both. Many people with gallstones have no symptoms, but when stones block the bile ducts, they can cause significant pain and digestive problems.
Symptoms
Gallstones often do not cause symptoms until they interfere with bile flow. When symptoms occur, they may include:
-
Sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen
-
Pain that may spread to the back or right shoulder
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Abdominal bloating or indigestion
-
Pain that worsens after eating fatty foods
-
Fever or chills if infection develops
Causes
Gallstones develop when bile contains too much cholesterol or bilirubin, or when the gallbladder does not empty completely. Common causes include:
-
Excess cholesterol in bile
-
Imbalance of bile salts
-
Poor gallbladder emptying
-
Liver conditions that increase bilirubin levels
These changes allow crystals to form, which can grow into stones over time.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of gallstone formation, including:
-
Being overweight or obese
-
Rapid weight loss or fasting
-
Pregnancy
-
Increasing age
-
Female sex
-
Family history of gallstones
-
Certain medical conditions such as diabetes
Complications
If gallstones block bile ducts or cause inflammation, complications may arise, such as:
-
Gallbladder inflammation known as cholecystitis
-
Bile duct infection
-
Pancreatitis caused by bile duct blockage
-
Gallbladder rupture in severe cases
Prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications.
Prevention
Although gallstones cannot always be prevented, the following measures may reduce risk:
-
Maintaining a healthy and stable body weight
-
Avoiding rapid weight loss diets
-
Eating regular, balanced meals
-
Including fiber-rich foods in the diet
-
Staying physically active
Early medical evaluation for abdominal pain can help detect gallstones before complications develop.
Advertisement