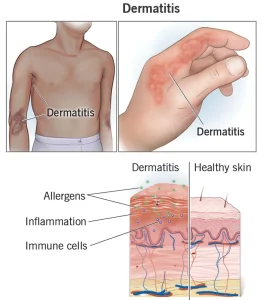
Overview
Dermatitis is a general term used to describe inflammation of the skin that results in redness, itching, and irritation. It can affect people of all ages and may be acute or chronic in nature. Dermatitis is not contagious and can occur due to allergic reactions, irritants, genetic factors, or underlying medical conditions. Common types include atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of dermatitis vary depending on the type and severity:
-
Red, inflamed skin
-
Itching, which may be mild to severe
-
Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
-
Swelling or tenderness
-
Blisters or oozing in acute cases
-
Thickened skin in chronic conditions
-
Burning or stinging sensation
Causes
Dermatitis develops due to skin barrier disruption and inflammatory responses:
-
Contact with irritants such as soaps, chemicals, or detergents
-
Allergic reactions to substances like metals, cosmetics, or plants
-
Genetic predisposition affecting skin barrier function
-
Immune system overactivity
-
Environmental factors such as extreme temperatures
-
Microbial overgrowth on the skin
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing dermatitis:
-
Personal or family history of allergies or asthma
-
Sensitive skin
-
Occupational exposure to irritants
-
Frequent hand washing or water exposure
-
Stress and hormonal changes
-
Living in dry or cold climates
Complications
If not properly managed, dermatitis can lead to:
-
Skin infections due to scratching
-
Chronic itching and discomfort
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Skin thickening or discoloration
-
Reduced self-esteem or emotional distress
-
Interference with daily activities
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on protecting the skin and reducing triggers:
-
Identifying and avoiding known irritants or allergens
-
Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products
-
Keeping skin well moisturized
-
Wearing protective clothing when exposed to irritants
-
Managing stress effectively
-
Maintaining proper skin hygiene without over-washing
Advertisement