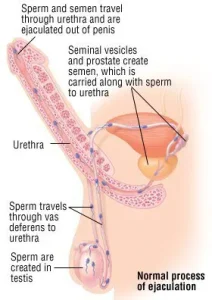
Overview
Delayed ejaculation is a male sexual dysfunction in which ejaculation takes an unusually long time to occur or does not occur at all despite adequate sexual stimulation and arousal. The condition can be lifelong or acquired later in life and may occur in specific situations or consistently. Delayed ejaculation can cause distress, affect intimate relationships, and reduce overall sexual satisfaction.
Symptoms
Symptoms of delayed ejaculation vary in severity and frequency:
-
Prolonged time required to ejaculate during sexual activity
-
Inability to ejaculate despite sufficient erection and stimulation
-
Reduced sexual satisfaction or frustration
-
Fatigue or discomfort during prolonged intercourse
-
Difficulty achieving ejaculation with a partner but not during masturbation
-
Emotional distress or relationship strain related to sexual performance
Causes
Delayed ejaculation can result from a combination of physical, psychological, and medication-related factors:
-
Nerve damage affecting ejaculation pathways
-
Hormonal imbalances, including low testosterone
-
Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes or multiple sclerosis
-
Side effects of medications, especially antidepressants
-
Psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, or stress
-
Relationship issues or performance-related concerns
-
Excessive alcohol consumption
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of delayed ejaculation include:
-
Increasing age
-
Use of certain medications affecting sexual function
-
Chronic illnesses affecting nerves or hormones
-
Mental health conditions
-
History of pelvic surgery or spinal injury
-
Substance use, including alcohol or recreational drugs
Complications
If delayed ejaculation persists, it may lead to several complications:
-
Reduced sexual satisfaction for the individual and partner
-
Difficulty conceiving due to ejaculation issues
-
Relationship conflicts or emotional distress
-
Decreased self-esteem
-
Avoidance of sexual intimacy
Prevention
Preventive strategies focus on addressing underlying causes and promoting sexual health:
-
Managing chronic medical conditions effectively
-
Reviewing medications with a healthcare provider
-
Limiting alcohol and substance use
-
Addressing psychological stress or anxiety through counseling
-
Maintaining open communication with sexual partners
-
Seeking early medical evaluation for persistent symptoms
Advertisement