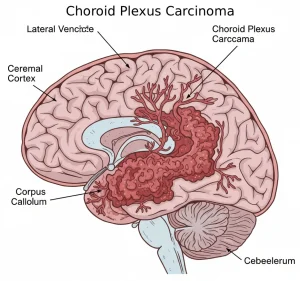
Overview
Choroid plexus carcinoma is a rare and aggressive malignant brain tumor that originates from the choroid plexus, a structure within the brain ventricles responsible for producing cerebrospinal fluid. This condition primarily affects infants and young children, though it can occur rarely in adults. Due to its rapid growth and tendency to spread within the central nervous system, choroid plexus carcinoma requires prompt diagnosis and intensive treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms are mainly caused by increased pressure inside the skull and disruption of normal brain function.
Common symptoms include:
-
Head enlargement in infants
-
Persistent headache
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Irritability or behavioral changes
-
Seizures
-
Poor feeding in infants
Other possible symptoms include:
-
Vision problems
-
Balance or coordination difficulties
-
Developmental delays
Causes
The exact cause of choroid plexus carcinoma is not fully understood. It develops due to abnormal and uncontrolled growth of choroid plexus epithelial cells.
Possible causes and contributing factors include:
-
Genetic mutations affecting cell regulation
-
Abnormal brain cell development
-
Association with inherited cancer predisposition syndromes
In many cases, the condition occurs sporadically without a clear external trigger.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing choroid plexus carcinoma.
Key risk factors include:
-
Early childhood, particularly infancy
-
Genetic conditions such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome
-
Family history of brain tumors
This cancer is rare, even among high-risk groups.
Complications
Choroid plexus carcinoma can lead to serious neurological and systemic complications if not treated promptly.
Possible complications include:
-
Hydrocephalus due to excess cerebrospinal fluid
-
Increased intracranial pressure
-
Neurological deficits such as weakness or cognitive impairment
-
Spread of cancer within the brain and spinal cord
-
Treatment-related complications from surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation
Long-term effects may persist even after successful treatment.
Prevention
There is no proven way to prevent choroid plexus carcinoma, but early detection and genetic awareness may improve outcomes.
Preventive and management strategies include:
-
Early evaluation of neurological symptoms in infants and children
-
Genetic counseling for families with known cancer syndromes
-
Regular medical follow-up for high-risk individuals
-
Prompt treatment to reduce tumor progression and complications
Early diagnosis and specialized medical care are critical for improving survival and quality of life in individuals with choroid plexus carcinoma.
Advertisement